In a second-hand bookshop, I found a copy of Moshe Feldenkrais’ Higher Judo: Groundwork (1952) as a gift for a friend. But (of course) I couldn’t resist having a quick look inside for myself, before giving it away! [You can read the whole book for yourself here]
Nowadays this author is best known as the founder of the Feldenkrais Method, which teaches healthy use of the body not through prescriptive instructions or strenuous exercise, but by developing your own sub-conscious self-awareness as well as your active proprioception. A typical “Awareness through Movement” session has you repeat simple, slow movements without undue effort, but with mindful attention. There is plenty of time between movements, not so much to rest, as to give your somatic nervous system time to ‘learn’ new connections. There is careful attention to breathing. Most participants find the sessions relaxing and undemanding (except of their attention), and are amazed at the positive effects they observe at the end. Typically, ease of movement, range of movement, balance and flow are greatly increased, with a strong accompanying sense of mental and spiritual well-being. I strongly recommend it. [Read more about the Feldenkrais Method here]
But Feldenkrais was also one of the first Western practioners of Judo, and he was held in high regard by Japanese masters of the Art. Gunji Koizumi, who brought Judo to the UK, wrote the preface to Feldenkrais’ book:
Dr M Feldenkrais has made a serious study of the subject, himself attaining Black Belt efficiency. He has studied and analysed Judo as a scientist in the light of the laws of physics, physiology and psychology, and he reports the results in this book which is enlightening and satisfying to the scientific mind of our age. Such a study has been long awaited and is a very valuable contribution to the fuller understanding and appreciation of the merits of Judo…
Dr Feldenkrais, with his learned mind, keen observation and masterly command of words, clarifies the interrelation and the intermingled working of gravitation, body, bones, muscles, nerves, consciousness, subconscious and un-consciousness and opens the way for better understanding.
As we might expect from a thinker who invented his own Method of Awareness through Movement, Feldenkrais’ idea of Groundwork goes far beyond the technicalities of holds, locks and other moves for fighting on the ground. His concept of Higher Judo applies a holistic approach with benefits for mind and spirit, as well as for the body.
Judo is the art of using all parts of the body to promote general well-being, and might be considered as a basic culture of the body. It creates a sense of rhythm of movement and co-ordination of mind and body. Soon after commencing practice, the novice often becomes aware of an improvement in his own occupation or sport, due to a sharpening of his senses.
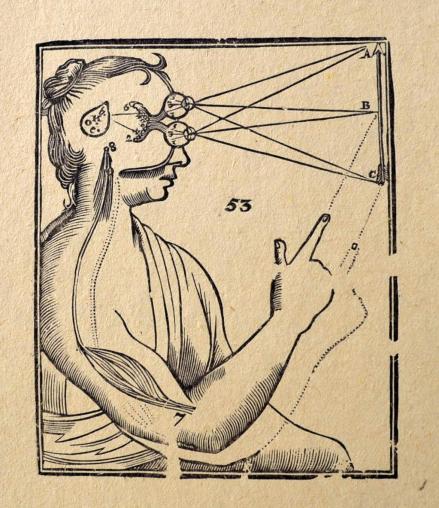
As part of this sharpening of the senses, Feldenkrais considers a question that equally concerns actors, opera-singers and indeed any performer: how do you perceive your own location in space, where are YOU? According to E. Claparède Notes sur la localisation du Moi (Archives de la Psychologie XIX 1924 p172)
We generally localise the ego at the base of the forehead, between the eyes.
I stumbled on this question as a teenager, and my own observations then confirmed Claparède’s findings. And before reading on, you might like to consider, perhaps even experiment with your own sense of where YOU are. If you lift your hand above your head, it is definitely above YOU, your feet are probably below YOU. Can you close in those limits to home-in on your personal sense of where YOU are located?
As Feldenkrais writes, “the localisation of the ego is not an anatomical fact, but is based on subjective accounts, and is, therefore, one of those things which has little significance unless other phenomena or facts can be aligned with it. It is certainly true that most people feel the ego, i.e. the point which feels more like “I”, at the base of the forehead between the eyes. But it is not exclusively so. With the advancement towards fuller maturity of the spatial and gravitational functions, the subjective feeling is that the ego gradually descends to be finally located somewhat below the navel.”
With fuller maturity, as acheived by Judo training, and by some people by their own means, subjects have no hesitation in finding the localisation in the lower abdomen.
When I mentioned this to a couple of experts in European Historical Swordsmanship, they too had no hesitation in agreeing with Feldenkrais’ location of the self. Stage performers similarly seek a sense of being “centred” or “grounded”.
For many years, I have practiced and taught a technique of ‘grounding’ for historical harp, counter-balancing the tendency for the action to be all ‘at the end of your fingertips’ and connecting-in the whole body, with a sense of centre and a pathway to the ground. And I rediscovered the importance of such ‘groundwork’ when I began research and practical investigation into baroque gesture.
But we know all too well the opposite feeling: instead of a calm centre, there are ‘butterflies in the stomach’, your ‘heart is in your mouth’, ‘the rug is taken out from under your feet’. The opposite of being centred and grounded is to be nervous and off-balance.
Feldenkrais again: “It may be interesting to note that nervous people are very undecided as to where they feel their “I” to be. Sometimes they declare it to be placed in accordance with Clarapède and sometimes they just cannot tell. In acute states of emotional disorder the sensation is that ego shifts between the two extreme localisations mentioned. When we are in good form, the lower localisation is more frequent, and is exclusively so with the higher exponents of Judo. The reader is warned that these observations must be considered critically, though we can demonstrate that we are better co-ordinated when we have no hesitation, and feel distinctly that our ego is located in the lower abdomen.”
Western Historical Martial Arts expert and author of several books on Historical Swordsmanship, Guy Windsor (principal of the School of European Swordsmanship in Helsinki) added the observation that, after a day spent researching and writing, he is aware of the sensation of being ‘too much in his head’, and welcomes the change of his own sense of location-of-self when he turns to training practice.
So we artists, whether performing or martial, are better co-ordinated, confident and in good form when we can ‘ground’ or ‘centre’ ourselves around the centre of gravity of the body. Depression, nervousness and other disturbances to our spiritual and mental balance, even too much intellectualising, all these can destabilise that centred feeling, but it can be re-established through training and practice.
Nevertheless, a question remains for those of us working in Historically Informed Performance. Whilst we expect an Oriental martial artist to be meditating on his breathing, mindful of the balance of his spirit, and contemplating a sense of self in his own navel (my gentle teasing is accompanied by the serious respect that this person probably knows 100 ways to kill me with minimal effort on his part); whilst we see that such holistic techniques can be very effective in modern theatre, in alternative medicine, in elite sport or in promoting mental health; whilst we may well see undeniable practical benefits in our own disciplines, is there any academic justification for introducing such ‘mumbo-jumbo’ into Historically Informed Performance? Where is the Western renaissance evidence to support concepts that we tend to associate with the Orient and with the 1960s?
According to period medical science, varying mental or spiritual states are reflected in the body as changes in the balance of the Four Humours, body liquids that produce visible signs and physical sensations of emotion. Excess of any Humour is unhealthy, but when we are in good form, we are inclined somewhat to the Sanguine Humour. Red blood warmed by the heart floods through the body to give us a healthy glow, a feeling of confidence and warm generosity, an appreciation of the pleasures of the belly (good food and red wine) as well as of the delights of music and dancing. Blood flows to the extremities so that we have good proprioception and muscles are warm, ready for action. In contrast, excess of the Melancholic Humour brings all the negative factors described above, and more: too much intellectualising, nervousness, depression, cold muscles, lack of sensitivity in the nerve-endings. The Melancholy person is ‘in their head’, the Sanguine person is ‘in their body’.
Modern experts in Alexander Technique and Feldenkrais Method, sports coaches and dancers, anyone with advanced understanding of physical movement can spot the ‘centred’ pose of a practitioner who is ‘relaxed and ready’, ‘grounded’ yet free to move. They can also spot the ability of a trained performer to structure their posture and movement so as to direct maximum efficacy into the desired result, with minimum effort. Renaissance paintings of dancers, swordsmen, even of passionate speakers or angel musicians show the same use of the body, the same relaxed movement and effortless strength that produce grazia of action and sprezzatura in performance, the very qualities so prized in a renaissance courtier. (See Il Libro del Cortegiano, The Book of the Courtier, here).
It is reasonable to assume that in a culture where people rode horses rather than driving cars, and danced or practised swordsmanship rather than playing computer games, Renaissance Man was not only fitter, but also more ‘centred’ than his modern counterpoint. Horse-riding, walking and running, dancing and swordfighting all promote proprioception, sense of balance and control of movement. Indeed, we might even assume that ‘centredness’ was the default state for a healthy person in that period – this would explain why period sources discuss the phenomenon mostly when it is pathologically absent.
Around the year 160q0, Italian sources frequently use the word vita (life) to mean also ‘the part of the body around the centre of gravity’. Dance-teacher Cesare Negri refers in Le Gratie d’Amore (1602) to walking well ‘sopra la vita‘ an effortlessly relaxed walk, with the body elegantly balanced over the centre of gravity. He also gives hilarious examples of how not to do it. “There are many different ways to walk, as we see every day on the street: some have the feet wide apart, and when they put a foot forwards, they fall from their centre of gravity onto this foot; others have the legs spread and the feet pointing outwards; others, when they put their feet forwards, wobble their belly backwards and forwards; others take lots of tiny fast steps with the points of toes outwards, as if they are on important business; others walk with their feet apart and their knees knocking together. All this offends the eyes of the onlookers. But to walk well, balanced on your core, with the best grace and ability, so that you give honour to others, is to walk well…
Colleagues of mine who are experts in Feldenkrais Method and Alexander Technique similarly recognise how mis-use of the body is reflected in the peculiarities of people’s gait.
One of the most dramatic moves in circa-1600 rapier fighting is the ‘scanso della vita‘, in which a fast, well-balanced turn removes the entire body from where your opponent was just about to stab you. This ‘voiding of the body-centre’ is accompanied by a counter-attack with the sword-hand in quarta.
This use of the word vita assures us that the seicento sense of a ‘body-centre’ was strong. But in that pre-Cartesian culture, there was no simple duality of mind and body. We might rather think of the Mind as centred Claparède-style between the eyes; the Spirits of Passion (higher emotions) centred at the heart; ‘gut-feelings’, posture and movement at the centre of gravity. All of these centres are linked by the ‘mystic breath’ of pneuma, the European renaissance’s analogue to oriental chi.
In this period, Music had a threefold identity: the divinely ordered movement of the stars and planets, musica mondana, the harmonious nature of the human body, musica humana, and actual music as performed on earth, musica instrumentalis (whether played or sung). Similarly, pneuma, the mystical Spirit of Passion, has a parallel three-fold nature as the divine breath of creation, the flow of breath/energy within the human body, and the communicative exchange between performer and audience. For a Historically Informed Performer, being ‘centred’ not only optimises your own physical co-ordination in performance and combats nervousness, but also empowers emotional communication to your audience, and puts both performer and audience in touch with the ineffable, mystical spark of artistic inspiration.
As Feldenkrais’ book title reminds us, in so many disciplines and in so many ways, Groundwork and the Higher Art are inextricably linked.
Please join me on Facebook https://www.facebook.com/andrew.lawrenceking.9 and visit our website www.TheHarpConsort.com .
Opera, orchestra, vocal & ensemble director and early harpist, Andrew Lawrence-King is director of The Harp Consort and of Il Corago, and Senior Visiting Research Fellow at the Australian Research Council Centre for the History of Emotions.




Please do you have a book reference I may check out?